A study design that reflected real-life, single-agent treatment choices
EMBRACE was the first Phase III trial in breast cancer to use Treatment of Physician's Choice (TPC) as a comparator arm1-3
EMBRACE: A PHASE III, RANDOMIZED, OPEN-LABEL, MULTICENTER, MULTINATIONAL TRIAL1,4
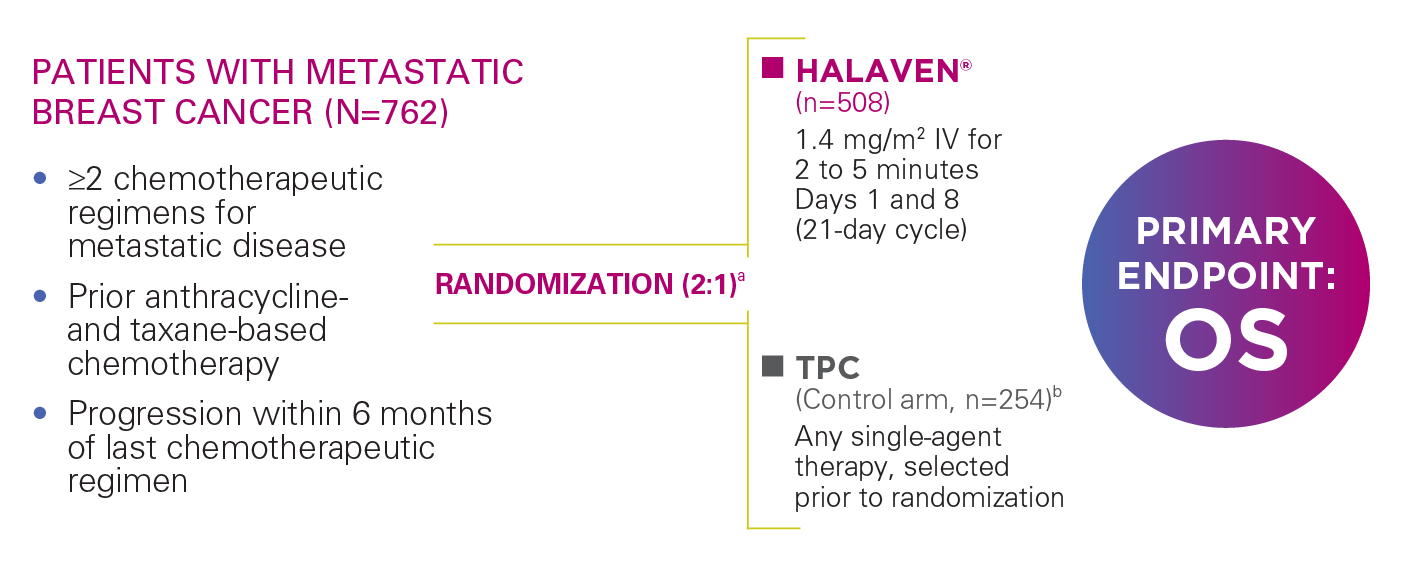
EMBRACE=Eisai Metastatic Breast Cancer Study Assessing Physician's Choice versus E7389 (Eribulin); IV=intravenous; OS=overall survival.
aRandomization was stratified by geographic region, HER2/neu status, and prior capecitabine exposure.4
bTherapies included in the TPC arm were determined prior to randomization to eliminate bias and had to be approved for the treatment of cancer, administered according to local practice, and available at time of study.1
OS STANDS AS THE HIGHEST STANDARD OF EVIDENCE FOR THE FDA IN THE ASSESSMENT OF CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS FOR CANCER REGIMENS5
THERAPIES IN THE TPC ARM4
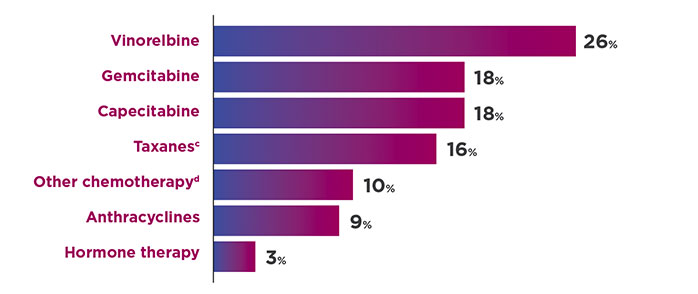
cIncluded paclitaxel, docetaxel, nab-paclitaxel, and ixabepilone.1
dIncluded cisplatin, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, mitomycin, fluorouracil, and methotrexate.1
Indications
Metastatic Breast Cancer
HALAVEN (eribulin mesylate) Injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who have previously received at least 2 chemotherapeutic regimens for the treatment of metastatic disease. Prior therapy should have included an anthracycline and a taxane in either the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Liposarcoma
HALAVEN is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma who have received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
Neutropenia: Severe neutropenia (ANC <500/mm3) lasting >1 week occurred in 12% of patients with mBC and liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 5% of patients with mBC and 2 patients (0.4%) died from complications. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 0.9% of patients with liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma, and fatal neutropenic sepsis occurred in 0.9% of patients. Patients with mBC with elevated liver enzymes >3 × ULN and bilirubin >1.5 × ULN experienced a higher incidence of Grade 4 neutropenia and febrile neutropenia than patients with normal levels. Monitor complete blood cell counts prior to each dose, and increase the frequency of monitoring in patients who develop Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias. Delay administration and reduce subsequent doses in patients who experience febrile neutropenia or Grade 4 neutropenia lasting >7 days.
Peripheral Neuropathy: Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 8% of patients with mBC (Grade 4=0.4%) and 22% developed a new or worsening neuropathy that had not recovered within a median follow-up duration of 269 days (range 25-662 days). Neuropathy lasting >1 year occurred in 5% of patients with mBC. Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 3.1% of patients with liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma receiving HALAVEN and neuropathy lasting more than 60 days occurred in 58% (38/65) of patients who had neuropathy at the last treatment visit. Patients should be monitored for signs of peripheral motor and sensory neuropathy. Withhold HALAVEN in patients who experience Grade 3 or 4 peripheral neuropathy until resolution to Grade 2 or less.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: HALAVEN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HALAVEN and for at least 2 weeks following the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HALAVEN and for 3.5 months following the final dose.
QT Prolongation: Monitor for prolonged QT intervals in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, drugs known to prolong the QT interval, and electrolyte abnormalities. Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to initiating HALAVEN and monitor these electrolytes periodically during therapy. Avoid in patients with congenital long QT syndrome.
Adverse Reactions
In patients with mBC receiving HALAVEN, the most common adverse reactions (≥25%) were neutropenia (82%), anemia (58%), asthenia/fatigue (54%), alopecia (45%), peripheral neuropathy (35%), nausea (35%), and constipation (25%). Febrile neutropenia (4%) and neutropenia (2%) were the most common serious adverse reactions. The most common adverse reaction resulting in discontinuation was peripheral neuropathy (5%).
In patients with liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma receiving HALAVEN, the most common adverse reactions (≥25%) reported in patients receiving HALAVEN were fatigue (62%), nausea (41%), alopecia (35%), constipation (32%), peripheral neuropathy (29%), abdominal pain (29%), and pyrexia (28%). The most common (≥5%) Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities reported in patients receiving HALAVEN were neutropenia (32%), hypokalemia (5.4%), and hypocalcemia (5%). Neutropenia (4.9%) and pyrexia (4.5%) were the most common serious adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation were fatigue and thrombocytopenia (0.9% each).
Use in Specific Populations
Lactation: Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from eribulin mesylate, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with HALAVEN and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
Hepatic and Renal Impairment: A reduction in starting dose is recommended for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment and/or moderate or severe renal impairment.
Indications
Metastatic Breast Cancer
HALAVEN (eribulin mesylate) Injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who have previously received at least 2 chemotherapeutic regimens for the treatment of metastatic disease. Prior therapy should have included an anthracycline and a taxane in either the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Liposarcoma
HALAVEN is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma who have received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.
Indications
Metastatic Breast Cancer
HALAVEN (eribulin mesylate) Injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who have previously received at least 2 chemotherapeutic regimens for the treatment of metastatic disease. Prior therapy should have included an anthracycline and a taxane in either the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Liposarcoma
HALAVEN is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma who have received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
Neutropenia: Severe neutropenia (ANC <500/mm3) lasting >1 week occurred in 12% of patients with mBC and liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 5% of patients with mBC and 2 patients (0.4%) died from complications. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 0.9% of patients with liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma, and fatal neutropenic sepsis occurred in 0.9% of patients. Patients with mBC with elevated liver enzymes >3 × ULN and bilirubin >1.5 × ULN experienced a higher incidence of Grade 4 neutropenia and febrile neutropenia than patients with normal levels. Monitor complete blood cell counts prior to each dose, and increase the frequency of monitoring in patients who develop Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias. Delay administration and reduce subsequent doses in patients who experience febrile neutropenia or Grade 4 neutropenia lasting >7 days.
Peripheral Neuropathy: Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 8% of patients with mBC (Grade 4=0.4%) and 22% developed a new or worsening neuropathy that had not recovered within a median follow-up duration of 269 days (range 25-662 days). Neuropathy lasting >1 year occurred in 5% of patients with mBC. Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 3.1% of patients with liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma receiving HALAVEN and neuropathy lasting more than 60 days occurred in 58% (38/65) of patients who had neuropathy at the last treatment visit. Patients should be monitored for signs of peripheral motor and sensory neuropathy. Withhold HALAVEN in patients who experience Grade 3 or 4 peripheral neuropathy until resolution to Grade 2 or less.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: HALAVEN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HALAVEN and for at least 2 weeks following the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HALAVEN and for 3.5 months following the final dose.
QT Prolongation: Monitor for prolonged QT intervals in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, drugs known to prolong the QT interval, and electrolyte abnormalities. Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to initiating HALAVEN and monitor these electrolytes periodically during therapy. Avoid in patients with congenital long QT syndrome.
Adverse Reactions
In patients with mBC receiving HALAVEN, the most common adverse reactions (≥25%) were neutropenia (82%), anemia (58%), asthenia/fatigue (54%), alopecia (45%), peripheral neuropathy (35%), nausea (35%), and constipation (25%). Febrile neutropenia (4%) and neutropenia (2%) were the most common serious adverse reactions. The most common adverse reaction resulting in discontinuation was peripheral neuropathy (5%).
In patients with liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma receiving HALAVEN, the most common adverse reactions (≥25%) reported in patients receiving HALAVEN were fatigue (62%), nausea (41%), alopecia (35%), constipation (32%), peripheral neuropathy (29%), abdominal pain (29%), and pyrexia (28%). The most common (≥5%) Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities reported in patients receiving HALAVEN were neutropenia (32%), hypokalemia (5.4%), and hypocalcemia (5%). Neutropenia (4.9%) and pyrexia (4.5%) were the most common serious adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation were fatigue and thrombocytopenia (0.9% each).
Use in Specific Populations
Lactation: Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from eribulin mesylate, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with HALAVEN and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
Hepatic and Renal Impairment: A reduction in starting dose is recommended for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment and/or moderate or severe renal impairment.
References: 1. Cortes J, O’Shaughnessy J, Loesch D, et al; EMBRACE (Eisai Metastatic Breast Cancer Study Assessing Physician’s Choice Versus E7389) investigators. Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): a phase 3 open-label randomised study. Lancet. 2011;377(9769):914-923. 2. Testori A, Richards J, Whitman E, et al. Phase III comparison of Vitespen, an autologous tumor-derived heat shock protein gp96 peptide complex vaccine, with physician's choice of treatment for stage IV melanoma: the C0100-21 study group. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(6):955-962. 3. Cree IA, Kurbacher CM, Lamont A, Hindley AC, Love S; TCA Ovarian Cancer Trial Group. A prospective randomized controlled trial of tumour chemosensitivity assay directed chemotherapy versus physician's choice in patients with recurrent platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2007;18(9):1093-1101. 4. HALAVEN [package insert]. Nutley, NJ: Eisai Inc. 5. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Clinical Trial Endpoints for the Approval of Cancer Drugs and Biologics. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm071590.pdf. Published May 2018. Accessed January 31, 2018.

